
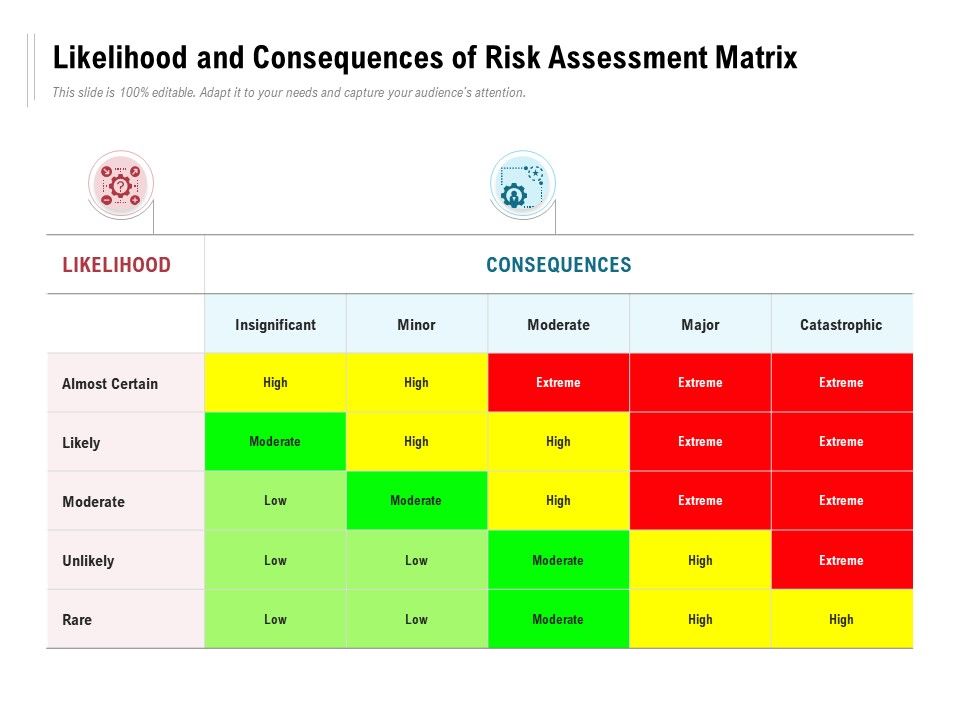
It is an adaptable approach, since it enables the adaptation of levels of impacts and the likelihood, as well as the acceptability associated with a specific objective in a specific situation. It is important to have some level of quantitative information and/or a good level of qualitative information available to do the assessment, as well as to understand well the consequences in order to structure the different levels of impacts efficiently. The facilitator needs to understand the basis of risk assessment, how this method operates and must be aware of how the descriptions in each of the tables are defined to assist the group to make good decisions about the most appropriate C × L combinations. So, for example, the same level of impact could be considered a moderate consequence for one objective but a high consequence for another.Īn experienced facilitator is required to make this system work efficiently. Moreover, the description of what level of impact is ascribed to what level of consequence can also vary. This should be changed to suit local circumstances, given that a level of impact may be acceptable in one circumstance but not in others. More information on the above matrix can be found below under Source of Information.Īdditionally, determining the acceptable level of impact is a very important part of the risk assessment (and management) process because it defines how the process operates. Additionally, the management response and the reporting requirements are addressed for each Risk category. The different coloured cells in the middle of the diagram represent the different Risk score (in brackets) and the Risk categories (No-Risk in blue Low-Risk in green Moderate-Risk in orange and High-Risk in red). Therefore increased management actions would be needed to achieve the objective.įigure 1: Risk analysis (Likelihood X Consequence) matrix with different levels of consequences or impacts at the top and the levels of probability or frequency on the left. These two scores are multiplied to generate a High Risk (9) which is an unacceptable level of risk. Using the Risk Matrix below, if the assessment group concludes that the most appropriate combination for the assessment of the Risk of a particular objective is that it is possible that a major consequence could occur, this is a Major Consequence (3) and a Possible Likelihood (3). This C x L risk assessment process involves selecting the most appropriate combination of consequence and likelihood levels that fit the situation for a particular objective based upon the information available and the collective knowledge of the group (including stakeholders, academics, managers, industry, researchers and technical staff) involved in the assessment process. Essentially, the higher the probability of a "worse" effect occurring, the greater the level of risk. The C × L matrix method therefore combines the scores from the qualitative or semi-quantitative ratings of consequence (levels of impact) and the likelihood (levels of probability) that a specific consequence will occur (not just any consequence) to generate a risk score and risk rating. Risk = Consequence x Likelihood where: (i) Likelihood is the Probability of occurrence of an impact that affects the environment and, (ii) Consequence is the Environmental impact if an event occurs. Risk assessment basically involves the calculation of the magnitude of potential consequences (levels of impacts) and the likelihood (levels of probability) of these consequences to occur. A quantitative risk assessment would require significantly more data which is very often an important constraint. The approach described below can only be used to calculate risk in a semi-quantitative or qualitative way. Identify critical knowledge gaps, thereby helping to prioritise future research.Facilitate explicit identification of environmental values of concern.Allow management agencies to ask "what if" questions regarding the consequences of various potential management actions.
Highlight the greatest risks needed to support allocation decisions for limited resources.The risk assessment is a useful management tool which will: In other words, it is the practice of assessing the impact of uncertainty on achieving objectives, organising information and contributing to the decision-making process. To perform a risk analysis to assess the risk of not achieving the goal set previously, as well as to identify and prioritise those issues where some necessary management actions could be required. Key Activity Scenario analysis (including risk assessment)


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
